/// 30 Jun 2025, 7:23 pm ////// FSF Blog ///
/// 30 Jun 2025, 4:29 pm ////// The Hacker News ///
/// 30 Jun 2025, 3:56 pm ////// Phoronix ///
This article focuses on selecting the best free astronomy software available for Linux.
The post 19 Best Free and Open Source Linux Astronomy Apps appeared first on LinuxLinks.
/// 30 Jun 2025, 6:38 pm ////// Google News ///
[link] [comments]
/// 30 Jun 2025, 3:59 pm ////// LINUXTODAY ///
We find a Linux distro that runs on computers big and small—and centers its identity on an antifascist stance—surprisingly refreshing!
The post antiX Linux: A ‘Proudly Anti-Fascist’ Distro That’s ‘Suitable for Old and New Computers’ appeared first on Linux Today.
/// 30 Jun 2025, 7:16 am ////// ITS FOSS ///

Retro techs are no longer stranger things. Just like vinyl records and vintage fashion, retro computing has captured our collective imagination, irrespective of the age group.
I mean, there's something deeply satisfying about amber-on-black terminals and chunky pixel fonts that modern UIs can't replicate.
The good thing here is that us Linux users are perfectly positioned to embrace this nostalgia wave.
No, I am not talking about those ultra-lightweight distros that involuntarily give retro vibes of late 90s and early 2000s. I am going to share a few interesting software that will help you get the retro feel on your modern Linux system.
1. Cool Retro Term
I'll start with my favorite, that is also a functional tool.
cool-retro-term is a terminal emulator which mimics the look and feel of the old cathode tube screens. That's just about it. You do not get any special abilities, just the good-old look.
But here's the thing. You can use it like your regular terminal, it have vintage looks but the modern features still work the same.
There are more than one presets of colors and style available.
Cool Retro Term
Installing Cool Retro Term
You can install it on Ubuntu, Fedora, and Arch Linux using the commands respectively:
sudo apt install cool-retro-term #For Debian/Ubuntu
sudo dnf install cool-retro-term #For Fedora
sudo pacman -Syu cool-retro-term #For Arch based distros2. RSC8
RSC8 is a CHIP-8 virtual machine/emulator written in Rust with no_std core. It is yet another makeover for your terminal. So, if you like to use a retro terminal but built with Rust, give this a try.
RSC8 Chip-8 Virtual machine/emulator
Install it using cargo.
cargo install --locked --git https://github.com/jerryshell/rsc8To use rsc8, you'll have to download ROMs of your choice from this GitHub repo and then use the following command:
rsc8_tui <your_rom.ch8>3. Retro Pie
RetroPie transforms your Raspberry Pi, ODroid C1/C2, or PC into a nostalgic gaming powerhouse.
It leverages platforms like Raspbian, EmulationStation, RetroArch, and other innovative projects, allowing you to enjoy classic Arcade, home-console, and vintage PC games with minimal hassle.
RetroPie Walkthrough
Since there were multiple kinds of platforms/consoles in the past, there are different emulators for them.
But that's only half of the story. You also need to download ROMs that consist of games of that platform.
For example, if you want to play games that were available Nintendo's NES console, you download the ROM with NES games and then use the NES emulator in RetroPi to load this ROM. It's like inserting a virtual disk.
The problem here is that these ROMs are often deemed illegal to distribute, and hence the websites that host them are often removed.
Playing Super Mario World in RetroPie
Installing RetroPi
Please ensure that you have git installed on your system as you'll have to clone the Git repo here.
cd
git clone --depth=1 https://github.com/RetroPie/RetroPie-Setup.gitRun the setup script:
cd RetroPie-Setup
sudo ./retropie_setup.shFollow the onscreen instructions for a basic installation.
4. Hot Dog Linux
Hot Dog Linux is an X11 Window Manager with Windows 3.1 Hot Dog Stand, Amiga Workbench, Atari ST GEM, Mac Classic and Aqua UI pre-installed.
HOTDOG is an acronym that stands for Horrible Obsolete Typeface and Dreadful Onscreen Graphics.
HOTDOG Linux
It is built using Objective-C and uses bitmapped graphics, low DPI displays. There are no unicode support here.
Installing Hot Dog Linux:
Download the ISO and install in VirtualBox. Make sure 3D acceleration is enabled.
5. DOSBox or DOSBox Staging
DOSBox is free and open-source software that allows you to emulate the MS-DOS operating systems from the previous century.
It allows you to play the 8-bit games.
Playing Doom2 in DOSBox
DOSBox also emulates CPU:286/386 realmode/protected mode, Directory FileSystem/XMS/EMS, Tandy/Hercules/CGA/EGA/VGA/VESA graphics, a SoundBlaster/Gravis Ultra Sound card for excellent sound compatibility with older games.
Installing DOSBox
On Ubuntu, and Arch, you can use the following commands respectively:
sudo apt install dosbox #For Ubuntu/Debina
sudo pacman -Syu dosbox #For ArchDOSBox Staging
Fedora ships with DOSBox Staging, a modern continuation of DOSBox. DOSBox Staging is also available in Flathub.
For Arch, it is in AUR. And, for Ubuntu and Mint, add the following PPA to get it installed:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:feignint/dosbox-staging
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt install dosbox-stagingWrapping Up
Linux enables users to have a godly amount of customization options. Whether you want your desktop to look clean, and contemporary, or you want to give it a retro look, there are certainly a few tools for that.
Come to think of, I should do a tutorial on how to give a retro makeover to your Linux distro, somewhat like the modern makeover video of Linux Mint.
Linux makes it easy to bring the retro vibe back to life. Whether it’s an old-school terminal, a full-blown vintage desktop, or classic games from the 90s, there’s a tool for every kind of nostalgia.
What is your favorite tool that we missed listing here? Let me know in the comments below.
/// 30 Jun 2025, 2:39 pm ////// 9to5Linux ///

digiKam 8.7 open-source professional photo management software is now available for download with various new features and improvements. Here's what's new!
The post digiKam 8.7 Adds New Tool to Perform Auto-Rotation Based on Content Analysis appeared first on 9to5Linux - do not reproduce this article without permission. This RSS feed is intended for readers, not scrapers.
/// 29 Jun 2025, 3:34 am ////// Slashdot ///
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
/// 30 Jun 2025, 12:32 pm ////// GamingOnLinux ///
 .
.
Read the full article on GamingOnLinux.
/// 30 Jun 2025, 2:31 pm ////// Superuser ///
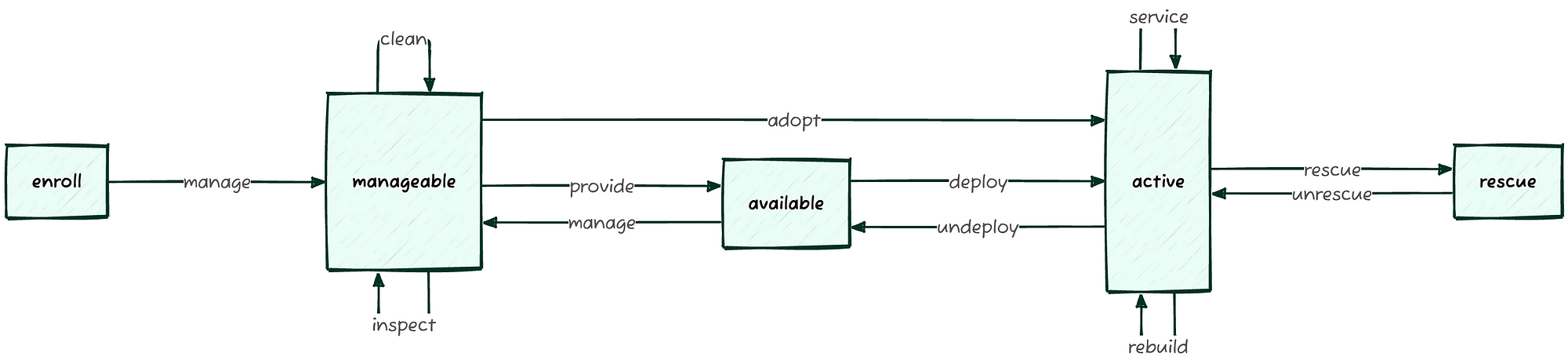
Managing physical servers as if they were Virtual Machines in a Cloud environment? Infrastructure-as-Code and CI/CD Pipelines with physical nodes? Let’s try to demystify some preconceptions about Private Cloud infrastructures and Bare Metal Lifecycle with practical, simple, and reproducible examples, starting with a minimal OpenStack Ironic “standalone” setup.
In our first post, we started to talk about bare metal lifecycle management by introducing OpenStack Ironic in a “standalone” configuration.
We laid the groundwork for our lab environment, detailing the minimal setup for the Bare Metal Service (bms) server, including the installation of Podman and the configuration of OpenStack Kolla Ansible. We covered the necessary steps to prepare the environment, install the Ironic Python Agent (IPA), and perform the initial OpenStack deployment.
3 Bare Metal Management
- Configuring the BMCs of the servers to be managed;
- Onboarding nodes;
- Inspecting nodes;
- Cleaning (optional);
- Deployment;
- Recovering an inaccessible node.
3.1 BMC Configuration
For Ironic to manage physical nodes, the various BMCs (Baseboard Management Controllers) must be accessible from the bms server via the OOB/IB network 172.19.74.0/24. (For the lab, a single LAN network, 192.168.0.0/24, where all services collapse, is also acceptable) with their respective access credentials.
The Ethernet card dedicated to operating system installation and in-band management must be PXE-boot enabled via the BIOS.
On many servers, the BMC’s MAC address and access credentials are listed on a dedicated label.
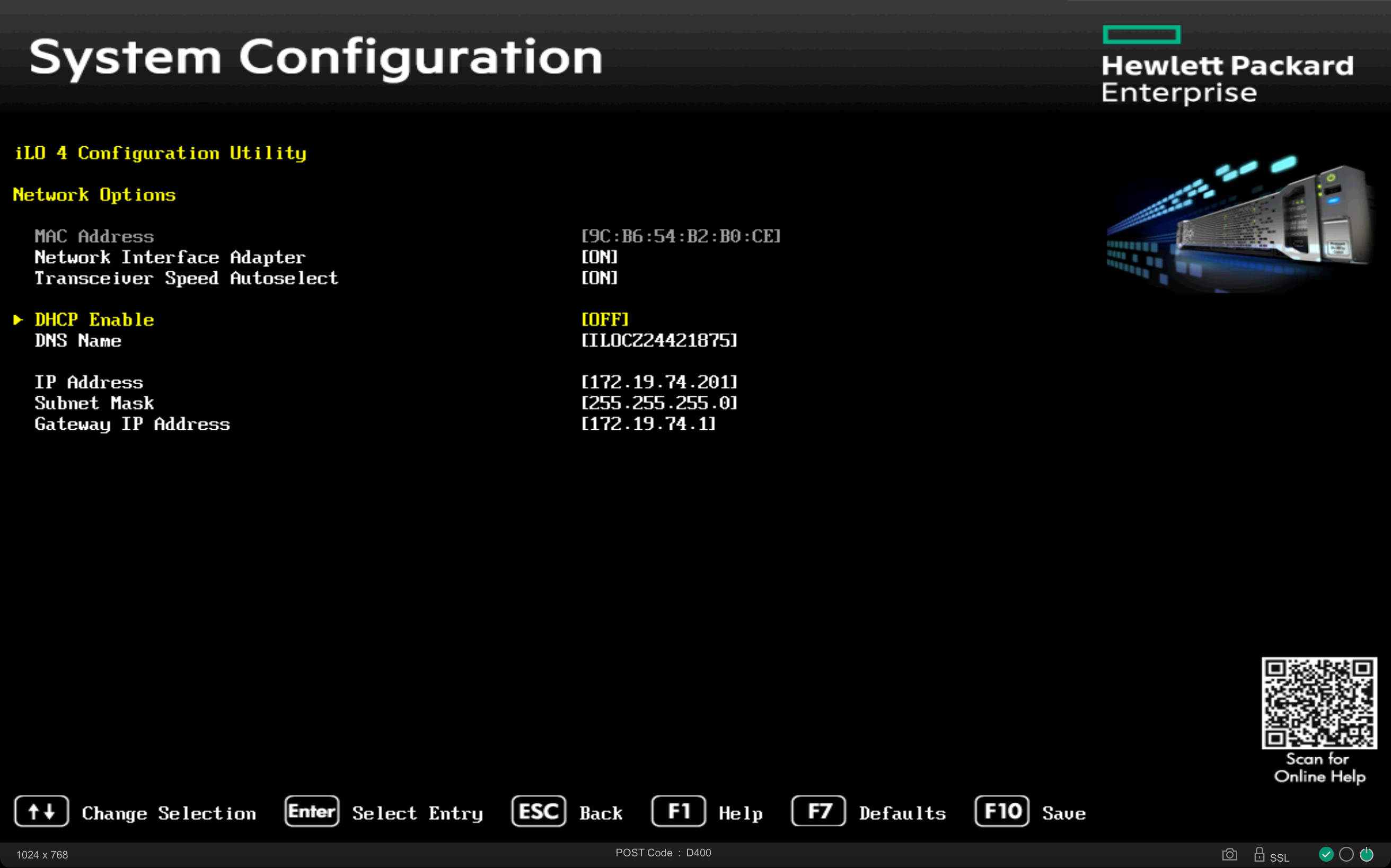
Let’s gather the information for the servers to be managed in a convenient location:
| Server | BMC address | BMC type | BMC user | BMC pass | PXE MAC address |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| server01 | 172.19.74.201 | redfish | ironic | baremetal | 9c:b6:54:b2:b0:ca |
| server02 | 172.19.74.202 | ipmi | ironic | baremetal | dc:f4:01:ec:7c:c4 |
| server03 | 172.19.74.203 | redfish | ironic | baremetal | 9c:b6:54:3a:55:10 |
To check if the BMCs are accessible via IPMI and/or Redfish protocols, let’s install the respective command-line tools:
kolla@bms:~$ sudo apt install ipmitool redfishtool
...
kolla@bms:~$ redfishtool -r 172.19.74.201 -u ironic -p baremetal Systems
{
"@odata.context": "/redfish/v1/$metadata#Systems",
"@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/Systems/",
"@odata.type": "#ComputerSystemCollection.ComputerSystemCollection",
"Description": "Computer Systems view",
"Members": [
{
"@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/Systems/1/"
}
],
"Members@odata.count": 1,
"Name": "Computer Systems"
}
kolla@bms:~$ ipmitool -C 3 -I lanplus -H 172.19.74.202 \
-U ironic -P baremetal chassis status
System Power : off
Power Overload : false
Power Interlock : inactive
Main Power Fault : false
Power Control Fault : false
Power Restore Policy : previous
Last Power Event :
Chassis Intrusion : inactive
Front-Panel Lockout : inactive
Drive Fault : false
Cooling/Fan Fault : false
Front Panel Control : none
NOTE: On some BMCs, using IPMI and Redfish protocols might require explicit enablement within the BIOS settings.
The enrollment phase occurs when a new server is onboarded and managed by Ironic using the command openstack baremetal node create --driver ....
The information required to proceed is:
- BMC type (e.g., ipmi, redfish, ilo, idrac, etc.)
- BMC IP address with its corresponding credentials (out-of-band)
- MAC address of the network card that will be used for inspection, installation, and potential recovery (in-band)
kolla@bms:~$ openstack baremetal node create \ --name server01 --driver redfish \ --driver-info redfish_address=https://172.19.74.201 \ --driver-info redfish_verify_ca=False \ --driver-info redfish_username=ironic \ --driver-info redfish_password=baremetal \ -f value -c uuid 5113ab44-faf2-4f76-bb41-ea8b14b7aa92 kolla@bms:~$ openstack baremetal node create \ --name server02 --driver ipmi \ --driver-info ipmi_address=172.19.74.202 \ --driver-info ipmi_username=ironic \ --driver-info ipmi_password=baremetal \ -f value -c uuid 5294ec18-0dae-449e-913e-24a0638af8e5 kolla@bms:~$ openstack baremetal node list +--------------------------------------+----------+---------------+-------------+--------------------+-------------+ | UUID | Name | Instance UUID | Power State | Provisioning State | Maintenance | +--------------------------------------+----------+---------------+-------------+--------------------+-------------+ | 5113ab44-faf2-4f76-bb41-ea8b14b7aa92 | server01 | None | None | enroll | False | | 5294ec18-0dae-449e-913e-24a0638af8e5 | server02 | None | None | enroll | False | +--------------------------------------+----------+---------------+-------------+--------------------+-------------+
To manage the servers, they must be declared manageable using the command openstack baremetal node manage ...:

Ironic will use the specified hardware driver (in this case, redfish) to query the BMC and will transition from the enrollstate to verifying, and finally to manageable, populating some server properties that can be queried with the command openstack baremetal node show <UUID|NAME> -f value -c properties.
kolla@bms:~$ openstack baremetal node manage server01
kolla@bms:~$ openstack baremetal node list
+--------------------------------------+----------+---------------+-------------+--------------------+-------------+
| UUID | Name | Instance UUID | Power State | Provisioning State | Maintenance |
+--------------------------------------+----------+---------------+-------------+--------------------+-------------+
| 5113ab44-faf2-4f76-bb41-ea8b14b7aa92 | server01 | None | power off | verifying | False |
| 5294ec18-0dae-449e-913e-24a0638af8e5 | server02 | None | None | enroll | False |
+--------------------------------------+----------+---------------+-------------+--------------------+-------------+
kolla@bms:~$ openstack baremetal node list
+--------------------------------------+----------+---------------+-------------+--------------------+-------------+
| UUID | Name | Instance UUID | Power State | Provisioning State | Maintenance |
+--------------------------------------+----------+---------------+-------------+--------------------+-------------+
| 5113ab44-faf2-4f76-bb41-ea8b14b7aa92 | server01 | None | power off | manageable | False |
| 5294ec18-0dae-449e-913e-24a0638af8e5 | server02 | None | None | enroll | False |
+--------------------------------------+----------+---------------+-------------+--------------------+-------------+
kolla@bms:~$ openstack baremetal node show server01 -f value -c properties
{'vendor': 'HPE'}
NOTE: Unfortunately, in this case, it’s not possible to use the “canonical” name (e.g., server01); you must explicitly use its corresponding UUID.
3.3 Inspection
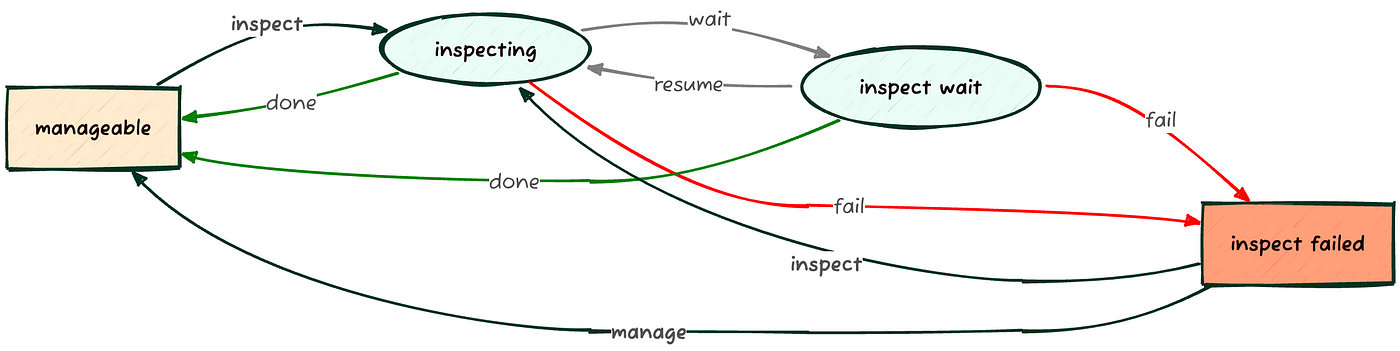
The “inspection” process in OpenStack Ironic is used to automatically catalog the hardware characteristics of a bare metal server.
This process allows us to gather various useful pieces of information, such as disks, CPU type, RAM, and network cards, before the actual installation. This data can then be used to guide and customize the installation itself.
kolla@bms:~$ time openstack baremetal node inspect server01 --wait Waiting for provision state manageable on node(s) server01 real 6m26.435s user 0m1.213s sys 0m0.073s
With the node inventory thus generated, you can inspect the node using the command openstack baremetal node inventory save <UUID|NAME>, which returns a JSON collection. To make it easier to interpret, it’s advisable to use the jq or yq command:
kolla@bms:~$ openstack baremetal node inventory save server01 | \ yq -r 'keys[]' inventory plugin_data kolla@bms:~$ openstack baremetal node inventory save server01 | \ yq -r '.inventory|keys[]' bmc_address bmc_mac bmc_v6address boot cpu disks hostname interfaces memory system_vendor kolla@bms:~$ openstack baremetal node inventory save server01 | \ yq -y '.inventory.system_vendor' product_name: ProLiant ML350 Gen9 (776971-035) serial_number: CZ24421875 manufacturer: HP firmware: vendor: HP version: P92 build_date: 08/29/2024 kolla@bms:~$ openstack baremetal node inventory save server01 | \ yq -y '.inventory.boot' current_boot_mode: uefi pxe_interface: 9c:b6:54:b2:b0:ca
To list the network cards and their characteristics, we could filter the output using the command yq -y '.inventory.interfaces', or even filter only the network cards that have a connected link (has_carrier==true):
kolla@bms:~$ openstack baremetal node inventory save server01 | \ yq -y '.inventory.interfaces|map_values(select(.has_carrier==true))' - name: eno1 mac_address: 9c:b6:54:b2:b0:ca ipv4_address: 172.19.74.193 ipv6_address: fe80::9eb6:54ff:feb2:b0ca%eno1 has_carrier: true lldp: null vendor: '0x14e4' product: '0x1657' client_id: null biosdevname: null speed_mbps: 1000 pci_address: '0000:02:00.0' driver: tg3 - name: eno2 mac_address: 9c:b6:54:b2:b0:cb ipv4_address: 192.168.0.195 ipv6_address: fe80::9eb6:54ff:feb2:b0cb%eno2 has_carrier: true lldp: null vendor: '0x14e4' product: '0x1657' client_id: null biosdevname: null speed_mbps: 1000 pci_address: '0000:02:00.1' driver: tg3
With this information, you can choose the best candidate disk on which to install the operating system. To specify the use of disk /dev/sdc, which is the SanDisk Ultra Fit of approximately 30GB with serial 4C530001220528100484, you can set the root_device property:
kolla@bms:~$ openstack baremetal node set server01 \
--property root_device='{"serial": "4C530001220528100484"}'
kolla@bms:~$ openstack baremetal node show server01 -f json | \
yq -y '.properties'
vendor: HPE
cpu_arch: x86_64
root_device:
serial: 4C530001220528100484
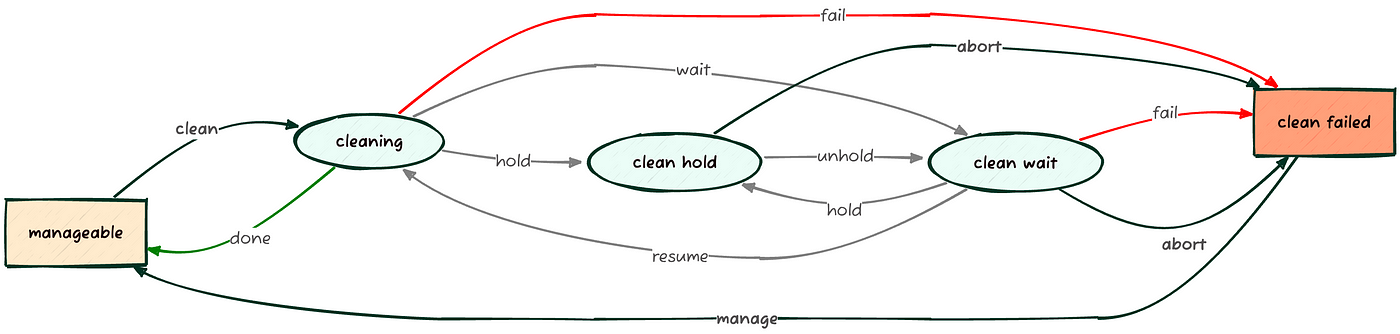
3.4 Cleaning (Optional)
If the hardware isn’t new, the disks might contain sensitive data or, worse, conflict with the new deployment (e.g., a previous operating system installed on a disk other than the intended destination).
To prevent these situations, it’s useful to use the node cleaning functionality provided by Ironic via the agent with the command openstack baremetal node clean <UUID>:
kolla@bms:~$ openstack baremetal node clean server01 \
--clean-steps '[{"interface": "deploy", "step": "erase_devices_metadata"}]'
The mandatory option --clean-steps is used to specify actions through a particular interface from the following: power, management, deploy, firmware, bios, and raid.
For the deploy interface, which is managed via the Ironic Python Agent (IPA), the available steps are:
erase_devices: Ensures data is wiped from disks.erase_devices_metadata: Wipes only disk metadata.erase_devices_express: Hardware-assisted data wiping, currently only supported by NVMe.
NOTE: For all other “cleaning” options, which we’ll skip for now (e.g., firmware upgrades, BIOS reset, RAID setup, etc.), you can refer to the Node Cleaning chapter in the Ironic documentation.
3.5 Deployment
Now that we’ve added, analyzed, and configured the systems to be managed (openstack baremetal node [create|manage|inspect|clean]), we’ll have a list of nodes in a manageable state:
kolla@bms:~$ openstack baremetal node list +--------------------------------------+----------+---------------+-------------+--------------------+-------------+ | UUID | Name | Instance UUID | Power State | Provisioning State | Maintenance | +--------------------------------------+----------+---------------+-------------+--------------------+-------------+ | 5113ab44-faf2-4f76-bb41-ea8b14b7aa92 | server01 | None | power off | manageable | False | | 5294ec18-0dae-449e-913e-24a0638af8e5 | server02 | None | power off | manageable | False | | f0d3f50a-d543-4e3d-9b9a-ba719373ab58 | server03 | None | power off | manageable | False | +--------------------------------------+----------+---------------+-------------+--------------------+-------------+
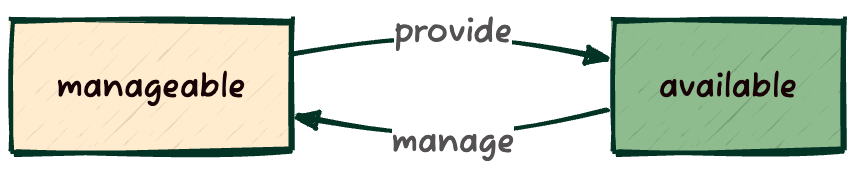
To make a physical node available for deployment, you need to declare it as available:
Any node in a manageable state is eligible to become available via the openstack baremetal node provide <UUID|NAME> command. The inverse operation is performed with openstack baremetal node manage <UUID|NAME>.
kolla@bms:~$ openstack baremetal node provide server01 kolla@bms:~$ openstack baremetal node list +--------------------------------------+----------+---------------+-------------+--------------------+-------------+ | UUID | Name | Instance UUID | Power State | Provisioning State | Maintenance | +--------------------------------------+----------+---------------+-------------+--------------------+-------------+ | 5113ab44-faf2-4f76-bb41-ea8b14b7aa92 | server01 | None | power off | available | False | | 5294ec18-0dae-449e-913e-24a0638af8e5 | server02 | None | power off | manageable | False | | f0d3f50a-d543-4e3d-9b9a-ba719373ab58 | server03 | None | power off | manageable | False | +--------------------------------------+----------+---------------+-------------+--------------------+-------------+ kolla@bms:~$ openstack baremetal node validate server01 +------------+--------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Interface | Result | Reason | +------------+--------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | bios | False | Driver redfish does not support bios (disabled or not implemented). | | boot | True | | | console | False | Driver redfish does not support console (disabled or not implemented). | | deploy | False | Node 5113ab44-faf2-4f76-bb41-ea8b14b7aa92 failed to validate deploy image info. Some | | | | parameters were missing. Missing are: ['instance_info.image_source'] | | firmware | False | Driver redfish does not support firmware (disabled or not implemented). | | inspect | True | | | management | True | | | network | True | | | power | True | | | raid | True | | | rescue | False | Node 5113ab44-faf2-4f76-bb41-ea8b14b7aa92 is missing 'instance_info/rescue_password'. It is | | | | required for rescuing node. | | storage | True | | +------------+--------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
We can perform a final check on the node to be installed using the openstack baremetal node validate <UUID|NAME>command (output shown above). The result indicates that some areas aren’t managed (False value):
- bios: In this case, the functionality was explicitly disabled with
enabled_bios_interfaces = no-bios. - console: This functionality is also disabled (
enabled_console_interfaces = no-console). - deploy: The
image_sourceparameter is missing, which specifies where to get the operating system image to install. - firmware: Functionality disabled (
enabled_firmware_interfaces = no-firmware). - rescue: The
rescue_passwordparameter is missing.
Without a surrounding Cloud environment, Ironic needs to know where to get the image to install, either directly via a file or a URL. The image_source parameter, in the --instance-info section of the openstack baremetal node setcommand, indicates exactly this.
Although it’s possible to use a URL on the Internet, for bandwidth optimization, it’s preferable to use a local repository. In this case, we’ll use the web server in the ironic_http container and the persistent ironic volume mounted to it:
kolla@bms:~$ sudo podman volume inspect ironic
[
{
"Name": "ironic",
"Driver": "local",
"Mountpoint": "/var/lib/containers/storage/volumes/ironic/_data",
"CreatedAt": "2025-04-02T18:28:15.831223385+02:00",
"Labels": {},
"Scope": "local",
"Options": {},
"MountCount": 0,
"NeedsCopyUp": true
}
]
kolla@bms:~$ sudo podman container inspect ironic_http | \
yq '.[]|.Mounts[]|select(.Name=="ironic")'
{
"Type": "volume",
"Name": "ironic",
"Source": "/var/lib/containers/storage/volumes/ironic/_data",
"Destination": "/var/lib/ironic",
"Driver": "local",
"Mode": "",
"Options": [
"nosuid",
"nodev",
"rbind"
],
"RW": true,
"Propagation": "rprivate"
}
kolla@bms:~$ sudo cat /etc/kolla/ironic-http/httpd.conf
Listen 172.19.74.1:8089
TraceEnable off
<VirtualHost *:8089>
LogLevel warn
ErrorLog "/var/log/kolla/ironic/ironic-http-error.log"
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b %D \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\"" logformat
CustomLog "/var/log/kolla/ironic/ironic-http-access.log" logformat
DocumentRoot "/var/lib/ironic/httpboot"
<Directory /var/lib/ironic/httpboot>
Options FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride None
Require all granted
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>
Since the volume /var/lib/containers/storage/volumes/ironic/_data is mounted under /var/lib/ironic in the ironic_http container and exposes the /var/lib/ironic/httpboot directory (DocumentRoot) via http://172.19.74.1:8089 (Listen), we can copy the various operating system images in raw or qcow2 format to the directory /var/lib/containers/storage/volumes/ironic/_data/httpboot/<IMAGE> and reference them as http://172.19.74.1:8089/<IMAGE>:
kolla@bms:~$ sudo wget \ -P /var/lib/containers/storage/volumes/ironic/_data/httpboot/ \ https://cloud.debian.org/images/cloud/bookworm/latest/debian-12-nocloud-amd64.qcow2 ... debian-12-nocloud-amd64.qcow2 100%[========================================>] 398.39M kolla@bms:~$ sudo wget \ -P /var/lib/containers/storage/volumes/ironic/_data/httpboot/ \ https://cloud.debian.org/images/cloud/bookworm/latest/debian-12-generic-amd64.qcow2 ... debian-12-generic-amd64.qcow2 100%[========================================>] 422.45M kolla@bms:~$ sudo podman exec --workdir=/var/lib/ironic/httpboot \ ironic_http sh -c 'sha256sum *.qcow2 >CHECKSUM' kolla@bms:~$ sudo podman exec ironic_http ls -la /var/lib/ironic/httpboot total 1202312 drwxr-xr-x 3 ironic ironic 4096 May 28 14:34 . drwxr-xr-x 8 ironic ironic 162 Apr 14 15:17 .. -rw-r--r-- 1 ironic ironic 1004 Apr 2 18:28 boot.ipxe -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 192 May 28 14:27 CHECKSUM -rw-r--r-- 1 ironic ironic 4843992 Apr 11 16:18 cp042886.exe -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 442970624 May 19 23:34 debian-12-generic-amd64.qcow2 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 417746432 May 19 23:50 debian-12-nocloud-amd64.qcow2 -rw-r--r-- 1 ironic ironic 8388608 May 27 17:37 esp.img -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 533 May 27 17:40 inspector.ipxe -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 348999425 May 27 17:40 ironic-agent.initramfs -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 8193984 May 27 17:40 ironic-agent.kernel drwxr-xr-x 2 ironic ironic 6 May 28 14:34 pxelinux.cfg kolla@bms:~$ curl -I http://172.19.74.1:8089/debian-12-nocloud-amd64.qcow2 HTTP/1.1 200 OK Date: Wed, 28 May 2025 10:46:31 GMT Server: Apache/2.4.62 (Debian) Last-Modified: Mon, 19 May 2025 21:50:09 GMT ETag: "18e64e00-635841d9c4640" Accept-Ranges: bytes Content-Length: 417746432
NOTE: Creating the CHECKSUM file is necessary to allow Ironic to verify that the image has not been altered during the transfer process from the source server to the bare metal node.
We’re ready to perform the first test deployment:
3.5.1 Test
As a first test, we can use the Debian Cloud image named “nocloud,” referenced as debian-12-nocloud-amd64.qcow2, to certify that the process works. Unfortunately, this image doesn’t have cloud-init installed, and it only allows root access directly from the console without a password, as the SSH service isn’t active.
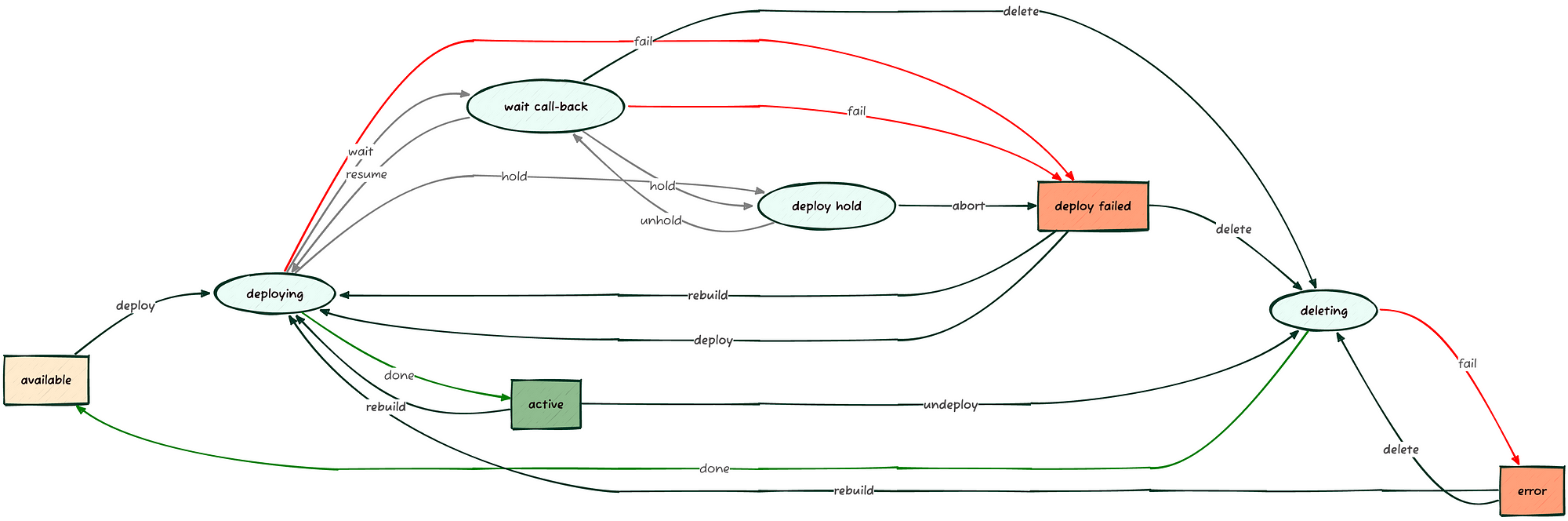
kolla@bms:~$ openstack baremetal node set server01 \ --instance-info image_source=http://172.19.74.1:8089/debian-12-nocloud-amd64.qcow2 \ --instance-info image_checksum=http://172.19.74.1:8089/CHECKSUM kolla@bms:~$ openstack baremetal node deploy server01 kolla@bms:~$ openstack baremetal node list +--------------------------------------+----------+---------------+-------------+--------------------+-------------+ | UUID | Name | Instance UUID | Power State | Provisioning State | Maintenance | +--------------------------------------+----------+---------------+-------------+--------------------+-------------+ | 5113ab44-faf2-4f76-bb41-ea8b14b7aa92 | server01 | None | power on | wait call-back | False | | 5294ec18-0dae-449e-913e-24a0638af8e5 | server02 | None | power off | manageable | False | | f0d3f50a-d543-4e3d-9b9a-ba719373ab58 | server03 | None | power off | manageable | False | +--------------------------------------+----------+---------------+-------------+--------------------+-------------+ kolla@bms:~$ openstack baremetal node list +--------------------------------------+----------+---------------+-------------+--------------------+-------------+ | UUID | Name | Instance UUID | Power State | Provisioning State | Maintenance | +--------------------------------------+----------+---------------+-------------+--------------------+-------------+ | 5113ab44-faf2-4f76-bb41-ea8b14b7aa92 | server01 | None | power on | deploying | False | | 5294ec18-0dae-449e-913e-24a0638af8e5 | server02 | None | power off | manageable | False | | f0d3f50a-d543-4e3d-9b9a-ba719373ab58 | server03 | None | power off | manageable | False | +--------------------------------------+----------+---------------+-------------+--------------------+-------------+ kolla@bms:~$ openstack baremetal node list +--------------------------------------+----------+---------------+-------------+--------------------+-------------+ | UUID | Name | Instance UUID | Power State | Provisioning State | Maintenance | +--------------------------------------+----------+---------------+-------------+--------------------+-------------+ | 5113ab44-faf2-4f76-bb41-ea8b14b7aa92 | server01 | None | power on | active | False | | 5294ec18-0dae-449e-913e-24a0638af8e5 | server02 | None | power off | manageable | False | | f0d3f50a-d543-4e3d-9b9a-ba719373ab58 | server03 | None | power off | manageable | False | +--------------------------------------+----------+---------------+-------------+--------------------+-------------+
Upon completion of the process, when the Provisioning State of the node in question becomes active, we can verify the outcome directly from the server’s console or via its BMC:
To decommission this test instance:
kolla@bms:~$ openstack baremetal node undeploy server01 kolla@bms:~$ openstack baremetal node list +--------------------------------------+----------+---------------+-------------+--------------------+-------------+ | UUID | Name | Instance UUID | Power State | Provisioning State | Maintenance | +--------------------------------------+----------+---------------+-------------+--------------------+-------------+ | 5113ab44-faf2-4f76-bb41-ea8b14b7aa92 | server01 | None | power on | deleting | False | | 5294ec18-0dae-449e-913e-24a0638af8e5 | server02 | None | power off | manageable | False | | f0d3f50a-d543-4e3d-9b9a-ba719373ab58 | server03 | None | power off | manageable | False | +--------------------------------------+----------+---------------+-------------+--------------------+-------------+ kolla@bms:~$ openstack baremetal node list +--------------------------------------+----------+---------------+-------------+--------------------+-------------+ | UUID | Name | Instance UUID | Power State | Provisioning State | Maintenance | +--------------------------------------+----------+---------------+-------------+--------------------+-------------+ | 5113ab44-faf2-4f76-bb41-ea8b14b7aa92 | server01 | None | power off | available | False | | 5294ec18-0dae-449e-913e-24a0638af8e5 | server02 | None | power off | manageable | False | | f0d3f50a-d543-4e3d-9b9a-ba719373ab58 | server03 | None | power off | manageable | False | +--------------------------------------+----------+---------------+-------------+--------------------+-------------+
The node will be powered off, and its Provisioning State will transition from active to deleting, and then back to available.
3.5.2 cloud-init
Static images, like the previous debian-12-nocloud, don’t provide configuration flexibility. Unless an image is specifically crafted to meet your needs (partitioning, networking, users, software, etc.), they tend to be of limited use.
We can achieve a compromise by using images that include cloud-init:
“Cloud images are OS templates and every instance starts as an identical clone of every other instance. It is the user data that gives each distinct cloud instance its personality, and cloud-init is the tool which applies user data to instances automatically.” (ref. https://cloud-init.io)
To provide personalization instructions to the bare metal node, we’ll use a portion of the node’s own disk, known as a Config Drive. During deployment, necessary information will be downloaded to this Config Drive in the form of structured files within a filesystem.
Assuming we want to install the server01 node with the following characteristics:
ironicuser with a pre-installed public SSH key andsudoprivileges to execute root commands;- Software to be automatically installed:
gitandpodman; - Network interface on the LAN configured with a static IP address
192.168.0.11/24, default gateway, and public DNS;
we can proceed as follows:
kolla@bms:~$ ssh-keygen
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/home/kolla/.ssh/id_rsa):
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
...
kolla@bms:~$ RSA_PUB=$(cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub)
kolla@bms:~$ NODE=server01
kolla@bms:~$ mkdir -p ~/ConfigDrive/$NODE/openstack/latest
kolla@bms:~$ cat >~/ConfigDrive/$NODE/openstack/latest/meta_data.json <<EOF
{
"uuid": "$(openstack baremetal node show $NODE -f value -c uuid)",
"hostname": "$NODE"
}
EOF
kolla@bms:~$ cat >~/ConfigDrive/$NODE/openstack/latest/user_data <<EOF
#cloud-config
package_update: true
packages:
- git
- podman
users:
- name: ironic
shell: /bin/bash
sudo: ["ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL"]
ssh_authorized_keys:
- '$RSA_PUB'
EOF
kolla@bms:~$ cat >~/ConfigDrive/$NODE/openstack/latest/network_data.json <<EOF
{
"links": [
{
"id": "oob0",
"type": "phy",
"ethernet_mac_address": "9c:b6:54:b2:b0:ca"
},
{
"id": "lan0",
"type": "phy",
"ethernet_mac_address": "9c:b6:54:b2:b0:cb"
}
],
"networks": [
{
"id": "oob",
"type": "ipv4_dhcp",
"link": "oob0",
"network_id": "oob"
},
{
"id": "lan",
"type": "ipv4",
"link": "lan0",
"ip_address": "192.168.0.11/24",
"gateway": "192.168.0.254",
"network_id": "lan"
}
],
"services": [
{
"type": "dns",
"address": "8.8.8.8"
},
{
"type": "dns",
"address": "8.8.4.4"
}
]
}
EOF
NOTE: For more information on the structure of the network_data.json file, refer to its schema: https://opendev.org/openstack/nova/src/branch/master/doc/api_schemas/network_data.json
To perform a new deployment leveraging cloud-init, we change the reference image_source to debian-12-generic-amd64.qcow2 and specify the directory containing the files to generate the Config Drive:
kolla@bms:~$ openstack baremetal node set server01 \ --instance-info image_source=http://172.19.74.1:8089/debian-12-generic-amd64.qcow2 \ --instance-info image_checksum=http://172.19.74.1:8089/CHECKSUM kolla@bms:~$ time openstack baremetal node deploy server01 \ --config-drive=$HOME/ConfigDrive/server01 --wait Waiting for provision state active on node(s) server01 real 12m3.542s user 0m0.863s sys 0m0.085s
NOTE: If we hadn’t already deleted the previous deployment with the openstack baremetal node undeploy <UUID|NAME> command, it’s still possible to reset the image_source variable using openstack baremetal node set <UUID|NAME> --instance-info image_source=... and then request a rebuild: openstack baremetal node rebuild <UUID|NAME> --config-drive=<PATH>.
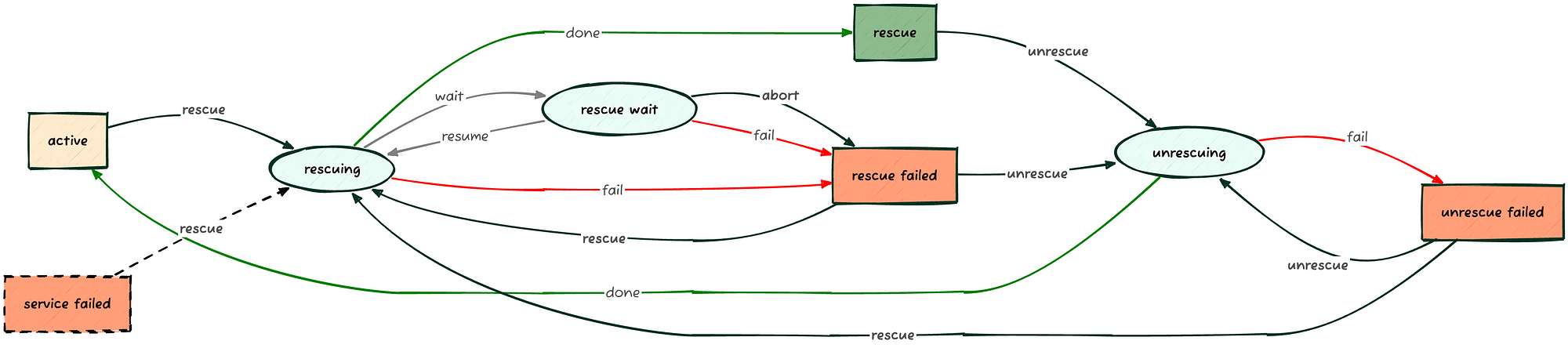
3.6 Recovering an Inaccessible Node (rescue)
Sometimes things go wrong… the IPA (Ironic Python Agent) loads, the operating system seems to write correctly to disk, and the Config Drive appears installed. Yet the node doesn’t boot, or maybe it boots, but the network card doesn’t configure, the admin user credentials seem incorrect, an error message flashes too quickly on the server monitor… in short, Murphy is always ready to contribute.
To leverage the IPA as a recovery system, the node must be in the active state and can be invoked with the following command:
kolla@bms:~$ openstack baremetal node show server01 -c provision_state +-----------------+--------+ | Field | Value | +-----------------+--------+ | provision_state | active | +-----------------+--------+ kolla@bms:~$ time baremetal node rescue server01 \ --rescue-password=<PASSWORD> --wait Waiting for provision state rescue on node(s) server01 real 5m42.284s user 0m0.745s sys 0m0.045s kolla@bms:~$ openstack baremetal node show server01 -c provision_state +-----------------+--------+ | Field | Value | +-----------------+--------+ | provision_state | rescue | +-----------------+--------+
We can identify the assigned IP address from the DHCP server logs of Ironic (which consists of a container running dnsmasq), starting from the MAC address of the network card used for deployment:
kolla@bms:~$ openstack baremetal port list -f value -c address \ --node $(openstack baremetal node show server01 -f value -c uuid) 9c:b6:54:b2:b0:ca kolla@bms:~$ sudo grep -i 9c:b6:54:b2:b0:ca /var/log/kolla/ironic/dnsmasq.log | tail -1 May 31 11:13:58 dnsmasq-dhcp[2]: DHCPACK(enp2s0) 172.19.74.192 9c:b6:54:b2:b0:ca
And finally, connect with the rescue user and the previously defined password to analyze the disk content, system and cloud-init logs, etc.:
kolla@bms:~$ ssh rescue@172.19.74.192 ... [rescue@localhost ~]$ sudo -i [root@localhost ~]# lsblk -o+fstype,label NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINTS FSTYPE LABEL sda 8:0 0 3.3T 0 disk sdb. 8:16 1 28.6G 0 disk |-sdb1 8:17 1 28.5G 0 part ext4 |-sdb2 8:18 1 64.4M 0 part iso9660 config-2 |-sdb14 8:30 1 3M 0 part `-sdb15 8:31 1 124M 0 part vfat sdc 8:32 0 838.3G 0 disk sr0 11:0 1 1024M 0 rom [root@localhost ~]# mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt [root@localhost ~]# mount --bind /dev /mnt/dev [root@localhost ~]# mount --bind /sys /mnt/sys [root@localhost ~]# mount --bind /proc /mnt/proc [root@localhost ~]# chroot /mnt root@localhost:/# journalctl --list-boots IDX BOOT ID FIRST ENTRY LAST ENTRY 0 34c9893dd3ab4a928207f7da41ec1226 Tue 2025-06-03 10:31:39 UTC Tue 2025-06-03 12:17:50 UTC root@localhost:/# journalctl -b 34c9893dd3ab4a928207f7da41ec1226 ... root@localhost:/# less /var/log/cloud-init.log ...
To check how the Config Drive was written:
[root@localhost ~]# mount -r LABEL=config-2 /media
[root@localhost ~]# find /media
/media
/media/openstack
/media/openstack/latest
/media/openstack/latest/meta_data.json
/media/openstack/latest/network_data.json
/media/openstack/latest/user_data
[root@localhost ~]# cat /media/openstack/latest/meta_data.json
{
"uuid": "5113ab44-faf2-4f76-bb41-ea8b14b7aa92",
"hostname": "server01"
}
[root@localhost ~]# cat /media/openstack/latest/user_data
#cloud-config
package_update: true
packages:
- git
- podman
users:
- name: ironic
shell: /bin/bash
sudo: ["ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL"]
ssh_authorized_keys:
- 'sha-rsa ...'
[root@localhost ~]# umount /media
NOTE: To exit the rescue state, DO NOT restart the system from within it (e.g., reboot, shutdown -r now, etc.); it would simply boot the operating system on the disk without changing the state in Ironic’s database. Instead, use the openstack baremetal node unrescue <UUID|NAME> command from the management server.
4 Automation and Infrastructure as Code
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) is an approach to IT infrastructure management where servers, networks, databases, and other components are defined and configured through code, rather than being created and managed manually. Infrastructure effectively becomes a set of declarative, versionable, and automatable files, allowing complex environments to be built in a repeatable, reliable, and scalable manner.
For demonstration purposes, among the hundreds of commercial and open-source projects addressing this topic, we will use two of the most well-known: Terraform and Ansible.
4.1 Terraform/OpenTofu
In this chapter, the main objective will be to reproduce the activities we’ve carried out so far on the command line to install the Debian 12 cloud image using Terraform/OpenTofu in the simplest and most straightforward way possible.
Terraform, developed by HashiCorp, is one of the most widely used tools for orchestrating cloud resources (AWS, Azure, GCP, OpenStack) and “traditional” environments (VMware, Proxmox, etc.). Its language allows for clearly and repeatably describing the resources needed for an infrastructure: servers, networks, DNS, firewalls, storage, and much more.
OpenTofu, born as a fork of Terraform after a license change by HashiCorp (recently acquired by IBM), fully maintains compatibility. Governed by the open-source community, its mission is to ensure that IaC remains open, accessible, and independent of commercial logic.
To install Terraform, follow the instructions at the following link: https://developer.hashicorp.com/terraform/install;
To install OpenTofu, run the command apt install -y tofu.
Let’s start by searching for a provider for OpenStack Ironic in their respective registries:
- Terraform: https://registry.terraform.io/browse/providers
- OpenTofu: https://search.opentofu.org/
We will find a common provider, supplied by Appkins Org and derived from the OpenShift project “Terraform provider for Ironic“: appkins-org/ironic.
Subsequently, in a directory specifically created to host Terraform/OpenTofu files, create a file named main.tf with the following content:
terraform {
required_providers {
ironic = {
source = "appkins-org/ironic"
version = "0.6.1"
}
}
}
provider "ironic" {
url = "http://172.19.74.1:6385/v1"
auth_strategy = "noauth"
microversion = "1.96"
timeout = 900
}
resource "ironic_node_v1" "server01" {
name = "server01"
inspect = true # Perform inspection
clean = false # Do not clean the node
available = true # Make the node 'available'
ports = [
{
"address" = "9c:b6:54:b2:b0:ca"
"pxe_enabled" = "true"
},
]
driver = "redfish"
driver_info = {
"redfish_address" = "https://172.19.74.201"
"redfish_verify_ca" = "False"
"redfish_username" = "ironic"
"redfish_password" = "baremetal"
}
}
resource "ironic_deployment" "server01" {
node_uuid = ironic_node_v1.server01.id
instance_info = {
image_source = "http://172.19.74.1:8089/debian-12-generic-amd64.qcow2"
image_checksum = "http://172.19.74.1:8089/CHECKSUM"
}
metadata = {
uuid = ironic_node_v1.server01.id
hostname = ironic_node_v1.server01.name
}
user_data = <<-EOT
#cloud-config
package_update: true
packages:
- git
- podman
users:
- name: ironic
shell: /bin/bash
sudo: ["ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL"]
ssh_authorized_keys:
- 'ssh-rsa ...'
EOT
}
In this file, besides specifying the appkins-org/ironic provider and its location, two resources are defined. The first, of type ironic_node_v1, represents the enrollment phase combined with the inspection phase. The second, of type ironic_deployment, will handle the deployment phase and the creation of the associated Config Drive.
To download the provider and its dependencies, simply call the Terraform/OpenTofu init procedure:
kolla@bms:~/TF$ terraform init - OR - kolla@bms:~/TF$ tofu init Initializing the backend... Initializing provider plugins... - Finding appkins-org/ironic versions matching "0.6.1"... - Installing appkins-org/ironic v0.6.1... - Installed appkins-org/ironic v0.6.1... ... Terraform/OpenTofu has been successfully initialized!
Meanwhile, to execute the actual deployment, you use the apply procedure:
kolla@bms:~/TF$ terraform apply - OR - kolla@bms:~/TF$ tofu apply ... Plan: 2 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy. Do you want to perform these actions? Terraform will perform the actions described above. Only 'yes' will be accepted to approve. Enter a value: yes ... ironic_deployment.server01: Creation complete after 10m32s [id=12016c80-be15-48ed-9b55-af00911c66b5] Apply complete! Resources: 2 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
4.2 Ansible
In this chapter, the goal is to achieve a more complex deployment that includes not only operating system provisioning but also the installation of a container orchestration platform like Kubernetes in an all-in-one (single node) setup.
Ansible is an open-source automation platform renowned for its incredible simplicity and remarkable power. Unlike other automation tools, Ansible is agentless, meaning it doesn’t require any additional software installation on the nodes it manages.
That said, other automation systems can be equally valid or even more suitable for your environment, such as Chef, Juju, Puppet, or SaltStack, to name just a few.
4.2.1 Ansible Playbook
The playbook structure will be as follows:
kolla@bms:~$ tree Ansible
Ansible
├── config.yml
├── deploy.yml
├── group_vars
│ └── all.yml
└── roles
├── ironic
│ └── tasks
│ └── main.yml
└── k8s-aio
├── defaults
│ └── main.yml
└── tasks
├── configure.yml
├── install.yml
├── main.yml
└── prepare.yml
8 directories, 9 files
In the config.yml file, we can create a data structure representing the list of nodes (nodes: []) to provision, trying to adhere as closely as possible to the form required by Ironic (bmc, root_device, instance_info, network_data, etc.), while adding some extra information like ansible_host and ansible_roles:
# config.yml
---
user_data: |
#cloud-config
users:
- name: {{ default_user }}
lock_passwd: false
sudo: ['ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL']
ssh_authorized_keys:
- '{{ public_key }}'
mounts:
- ['swap', null]
nodes:
- name: server01
ansible_host: "192.168.0.11"
ansible_roles:
- k8s-aio
bmc:
driver: redfish
driver_info:
redfish_address: "https://172.19.74.201"
redfish_verify_ca: false
redfish_username: "ironic"
redfish_password: "baremetal"
pxe:
mac: "9c:b6:54:b2:b0:ca"
root_device:
serial: "4C530001220528100484"
instance_info:
image_source: "http://172.19.74.1:8089/debian-12-generic-amd64.qcow2"
image_checksum: "http://172.19.74.1:8089/CHECKSUM"
network_data:
links:
- id: "oob0"
type: "phy"
ethernet_mac_address: "9c:b6:54:b2:b0:ca"
- id: "lan0"
type: "phy"
ethernet_mac_address: "9c:b6:54:b2:b0:cb"
networks:
- id: "oob"
type: "ipv4_dhcp"
link: "oob0"
network_id: "oob"
- id: "lan"
type: "ipv4"
link: "lan0"
ip_address: "192.168.0.11"
netmask: "255.255.255.0"
gateway: "192.168.0.254"
network_id: "lan"
services:
- type: "dns"
address: "8.8.8.8"
- type: "dns"
address: "8.8.4.4"
NOTE: Although the ansible_host variable is redundant (as it can be derived from processing the network_datastructure), it’s preferable to keep it explicit to improve playbook readability and avoid complex JSON Queries. If you prefer not to duplicate the information, you would still need to specify which interface to use for the connection (e.g., ansible_link: "lan0") to enable the query.
As a workaround to dynamically configure individual nodes, we’ll place the list of Ansible roles to apply to each node within the ansible_roles variable, as defined in the deploy.yml playbook:
# deploy.yml
---
- hosts: localhost
connection: local
gather_facts: true
tasks:
- name: Provision baremetal nodes
ansible.builtin.include_role:
name: ironic
loop: "{{ nodes }}"
loop_control:
loop_var: node
- hosts: ironic
gather_facts: false
tasks:
- name: Wait for node to become reachable
ansible.builtin.wait_for_connection:
- name: Gather facts for first time
ansible.builtin.setup:
- name: Provision node {{ ansible_hostname }}
ansible.builtin.include_role:
name: "{{ role }}"
loop: "{{ ansible_roles }}"
loop_control:
loop_var: role
You’ll notice two groups (under hosts: elements) on which actions will be performed:
localhost: Through this, we’ll control OpenStack Ironic via its API for each node defined in ourconfig.ymlconfiguration file.ironic: This is a dynamic group that will be formed as theironicrole from the first group completes the operating system deployment for a node.
4.2.2 The “ironic” Role
The ironic role (found in the roles/ironic subdirectory) includes the enrollment phase (using the openstack.cloud.baremetal_node module) and the actual deployment phase (using the openstack.cloud.baremetal_node_action module). It also handles adding the node itself to the ironic group in the inventory (using the ansible.builtin.add_host module):
# roles/ironic/tasks/main.yml
---
- name: "Enroll {{ node.name }}"
register: baremetal_create
openstack.cloud.baremetal_node:
cloud: "ironic-standalone"
driver: "{{ node.bmc.driver }}"
driver_info: "{{ node.bmc.driver_info }}"
name: "{{ node.name }}"
uuid: "{{ node.uuid|default(omit) }}"
nics:
- mac: "{{ node.pxe.mac }}"
properties:
capabilities: "boot_option:local"
root_device: "{{ node.root_device }}"
- name: "Deploy {{ node.name }}"
when: baremetal_create is changed
openstack.cloud.baremetal_node_action:
cloud: "ironic-standalone"
id: "{{ baremetal_create.node.id }}"
timeout: 1800
instance_info: "{{ node.instance_info }}"
config_drive:
meta_data:
uuid: "{{ baremetal_create.node.id }}"
hostname: "{{ node.name }}"
user_data: "{{ cloud_config }}"
network_data: "{{ node.network_data }}"
- name: "Add {{ node.name }} to inventory"
ansible.builtin.add_host:
name: "{{ node.name }}"
groups: ironic
ansible_host: "{{ node.ansible_host }}"
ansible_user: "{{ default_user }}"
ansible_ssh_extra_args: "-o StrictHostKeyChecking=no"
ansible_roles: "{{ node.ansible_roles }}"
Each module within the Openstack.Cloud collection uses the connection parameters referenced by the cloud variable, found in the ~/.config/openstack/clouds.yaml file (as discussed in Chapter 2.6, OpenStack Ironic “Standalone” Configuration in part 1).
Alternatively, instead of using the cloud parameter, you can explicitly specify the connection parameters:
- name: ...
openstack.cloud.baremetal_...:
auth:
endpoint: "http://172.19.74.1:6385"
auth_type: None
...
NOTE: The additional parameters -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no are necessary due to the potential overlap of SSH server certificates generated randomly with each deployment (if you delete and then redeploy the same server with the same IP address, the SSH server certificate will not be identical).
The creation of the ironic system user and the prevention of swap area activation (as required by Kubernetes) are addressed through the use of user_data with the cloud_config variable defined in the previous config.yml file.
4.2.3 The “k8s-aio” Role
The k8s-aio role (in the roles/k8s-aio subdirectory) has been structured to reproduce the Kubernetes installation phases described in the official documentation (Bootstrapping clusters with kubeadm), in addition to the Flannel CNI and the Nginx ingress controller.
For each physical node requiring this role, the actions contained in prepare.yml and install.yml will be executed in succession with privileged user rights, and configure.yml will be executed as the ironic user:
# roles/k8s-aio/tasks/main.yml
---
- name: Prepare server
ansible.builtin.include_tasks:
file: prepare.yml
apply:
become: true
- name: Install Kubernetes
ansible.builtin.include_tasks:
file: install.yml
apply:
become: true
- name: Configure Kubernetes
ansible.builtin.include_tasks:
file: configure.yml
The prepare.yml file focuses on system requirements, such as kernel modules to load, network parameters, and necessary software packages:
# roles/k8s-aio/tasks/prepare.yml
---
- name: Enable Kernel modules
community.general.modprobe:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: present
persistent: present
loop:
- overlay
- br_netfilter
- name: Setup networking stack
ansible.posix.sysctl:
name: "{{ item.name }}"
value: "{{ item.value }}"
sysctl_file: /etc/sysctl.d/kubernetes.conf
loop:
- name: net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables
value: 1
- name: net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables
value: 1
- name: net.ipv4.ip_forward
value: 1
- name: Install dependencies
ansible.builtin.apt:
pkg:
- apt-transport-https
- ca-certificates
- containerd
- curl
- gpg
- reserialize
update_cache: yes
The installation phase follows the rules described in the documentation, resulting in a single-node Kubernetes cluster that can respond via its standard APIs:
# roles/k8s-aio/tasks/install.yml
---
- name: Download the public key for Kubernetes repository
ansible.builtin.shell: |
curl -fsSL {{ k8s_pkgs_url }}/Release.key | \
gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/kubernetes.gpg
args:
creates: /etc/apt/keyrings/kubernetes.gpg
- name: Add Kubernetes APT repository
ansible.builtin.apt_repository:
repo: "deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/kubernetes.gpg] {{ k8s_pkgs_url }} /"
filename: kubernetes
state: present
- name: Install Kubernetes packages
ansible.builtin.apt:
pkg:
- jq
- kubeadm
- kubectl
- kubelet
- name: Check SystemdCgroup in containerd
register: systemd_cgroup
ansible.builtin.shell:
crictl info | \
jq -r '.config.containerd.runtimes.runc.options.SystemdCgroup'
- name: Enable SystemdCgroup in containerd
when: systemd_cgroup.stdout == "false"
ansible.builtin.shell: |
containerd config default | \
reserialize toml2json | \
jq '.plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".containerd.runtimes.runc.options.SystemdCgroup=true' | \
reserialize json2toml >/etc/containerd/config.toml
- name: Restart containerd service
when: systemd_cgroup.stdout == "false"
ansible.builtin.systemd_service:
name: containerd.service
state: restarted
- name: Pull the required Kubernetes images
ansible.builtin.command:
cmd: kubeadm config images pull
creates: /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf
- name: Initialize Kubernetes
ansible.builtin.command:
cmd: kubeadm init --pod-network-cidr={{ k8s_network }} --control-plane-endpoint {{ ansible_host }}:6443
creates: /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf
Finally, in the configuration phase, the non-administrative user completes the Kubernetes setup by installing Flannel and Ingress-Nginx:
# roles/k8s-aio/tasks/configure.yml
---
- name: Read /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf
become: true
register: kube_conf
ansible.builtin.slurp:
src: /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf
- name: Create ~/.kube
ansible.builtin.file:
path: ~/.kube
state: directory
mode: 0700
- name: Create ~/.kube/config
ansible.builtin.copy:
content: "{{ kube_conf['content']|b64decode }}"
dest: "~/.kube/config"
mode: 0600
- name: Install Flannel
# https://github.com/flannel-io/flannel?tab=readme-ov-file#deploying-flannel-with-kubectl
ansible.builtin.command:
cmd: kubectl apply -f https://github.com/flannel-io/flannel/releases/latest/download/kube-flannel.yml
- name: Remove NoSchedule taint for control-plane
failed_when: false
ansible.builtin.command:
cmd: kubectl taint nodes {{ ansible_hostname }} node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane:NoSchedule-
- name: Install Ingress-Nginx Controller
ansible.builtin.command:
cmd: kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/main/deploy/static/provider/cloud/deploy.yaml
Some default values for the k8s-aio role can be found in the roles/k8s-aio/defaults/main.yml file:
# roles/k8s-aio/defaults/main.yml
---
k8s_version: "1.33"
k8s_network: "10.244.0.0/16"
k8s_pkgs_url: "https://pkgs.k8s.io/core:/stable:/v{{ k8s_version }}/deb"
The playbook concludes with the global variables file, group_vars/all.yml, which contains the default value for the public SSH key, the default name of the user to create, the content of the user_data, and the initialization of the node list:
# group_vars/all.yml
---
public_key: "{{ lookup('file', '~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub') }}"
default_user: ironic
cloud_config: |
#cloud-config
users:
- name: {{ default_user }}
shell: /bin/bash
sudo: ['ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL']
ssh_authorized_keys:
- '{{ public_key }}'
nodes: []
4.2.4 Deployment
So, let’s launch the playbook with the command ansible-playbook -e @config.yml deploy.yaml:
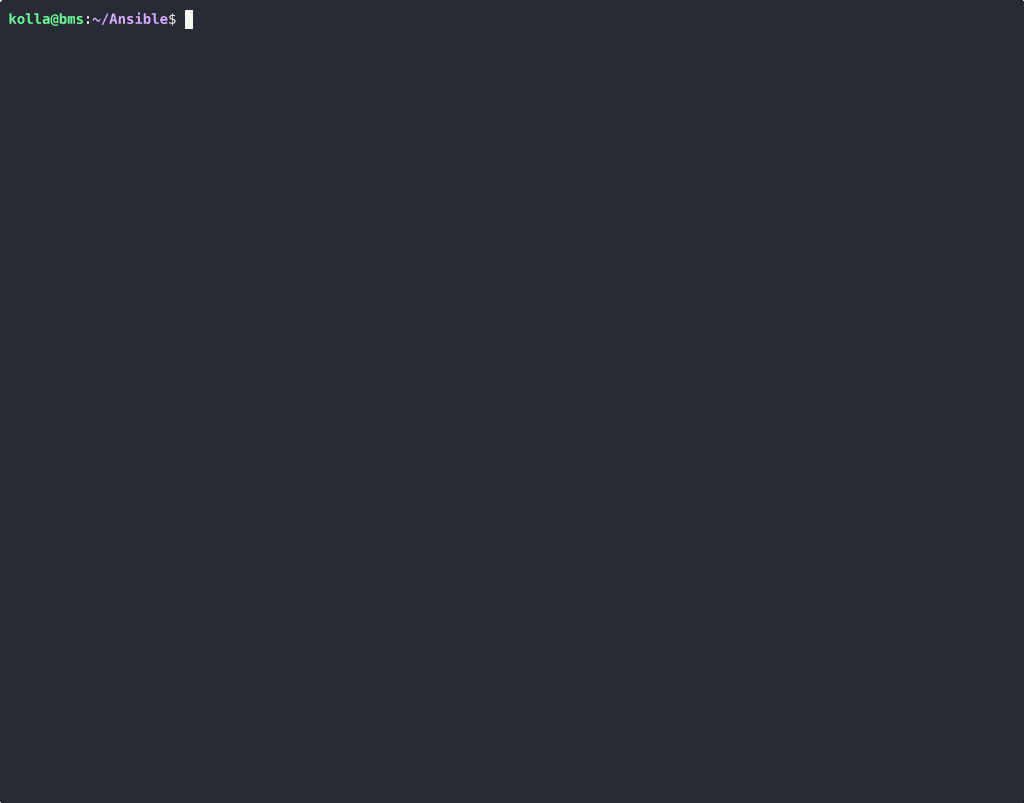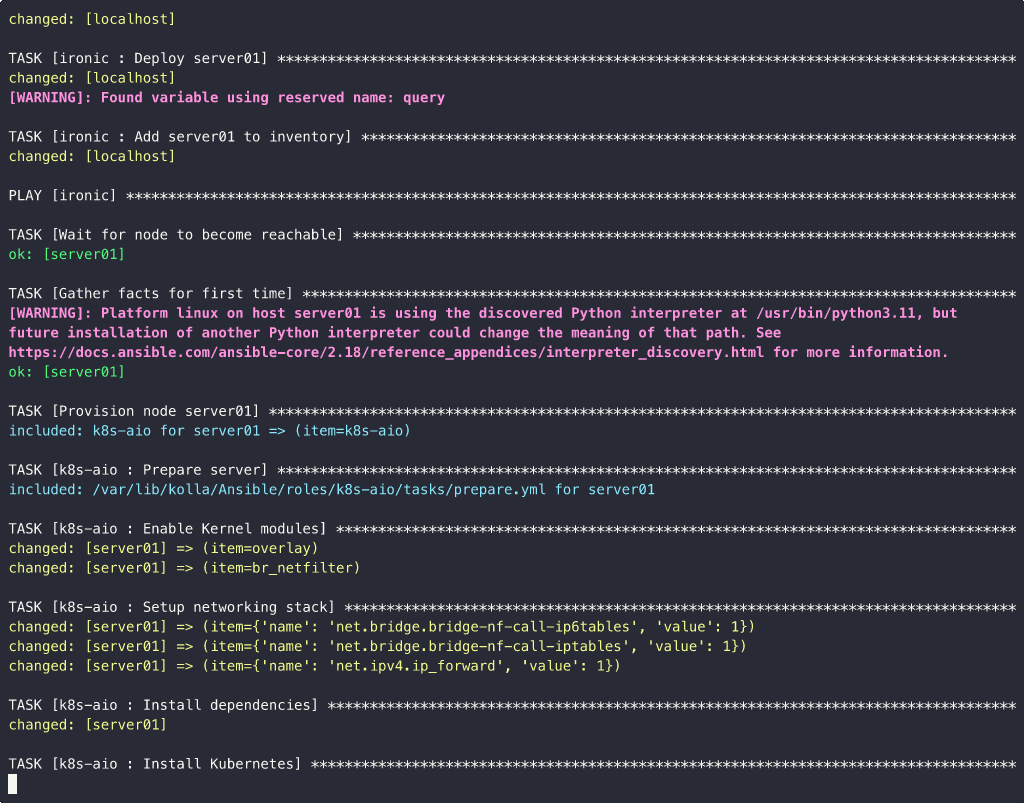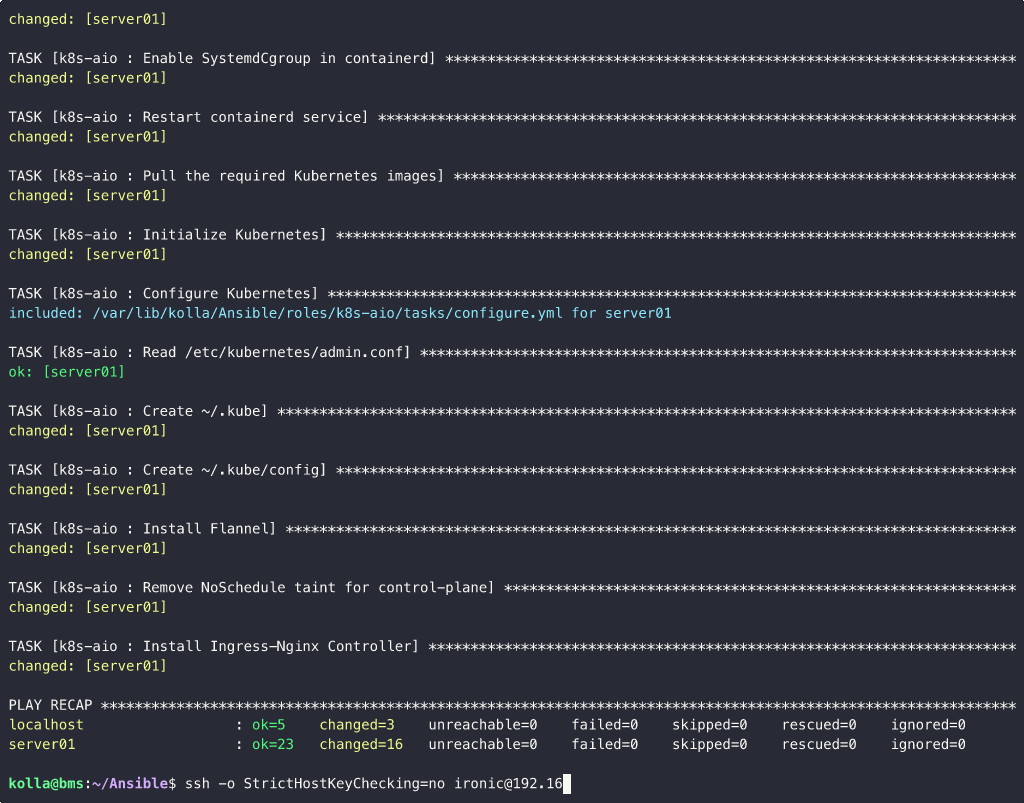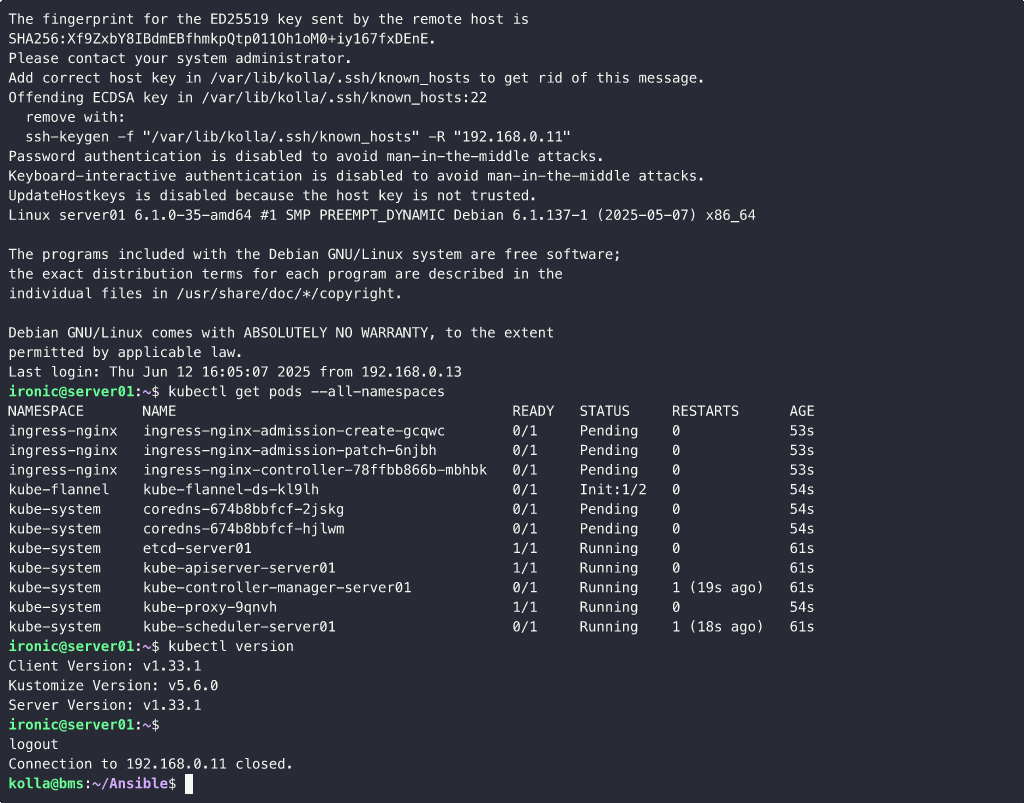
Some Considerations
Even though OpenStack Ironic was configured in a “standalone” mode, the availability of OS cloud-ready images that include cloud-init, combined with the use of Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) and Automation systems, allows for implementing effective Hardware Lifecycle management, application layer included.
The post Part Two: Getting Started with Standalone OpenStack Ironic appeared first on Superuser.
Review: AxOS 25.06 and 25.01, AlmaLinux OS 10.0
News: Ubuntu to boost Intel graphics performance, Fedora discusses dropping i686 packages, SDesk switches from SELinux to AppArmor
Questions and answers: Transferring Flatpak packages between computers
Released last week: postmarketOS 25.06, Escuelas Linux 8.12, IPFire 2.29 Core 195,....
/// 30 Jun 2025, 6:00 am ////// Tecmint ///
atop is a full-screen performance monitoring tool that provides detailed reports about all system processes, including those that have already
The post How to Install ‘atop’ to Monitor Real-Time System Performance first appeared on Tecmint: Linux Howtos, Tutorials & Guides.